Reasons and classification
development mechanism
- If the load is heavy and the joints are not given time to recover, nutrients are destroyed. Cartilage becomes thinner, cracks and ulcers appear;
- The structure of collagen fibers is destroyed and the absorption effect becomes poor. The cartilage and patella soften, become inelastic, and their function becomes worse;
- Bone growth occurs in the joints. The joint capsule becomes irritated and inflamed;
- As a person starts taking care of their knee and moves it less, less intra-joint fluid is produced. The cartilage surface becomes dry and rough;
- The knee receives less nutrients, atrophies, and destruction accelerates.
Stages of Arthropathy
- Early days. The organization has not been destroyed. So far, only the function of the synovial membrane is deteriorating. The composition of the intra-articular fluid changes. The knee can no longer bear normal loads;
- The articular cartilage and meniscus begin to deteriorate. Osteophytes (bone formations) grow into bones. Inflammation and pain occur;
- Difficult stage. The knee joint support platform deforms and the leg axis changes. The ligaments shorten and the joint capsule becomes stiff. The joint is pathologically mobile, but full flexion or straightening is not possible. Inflammation and pain are evident.
Please note! In the early stages of the disease, the muscles are intact. Their function is gradually lost. In phase three, activities are severely restricted. Due to changes in the axis of motion, muscle attachment sites change. Muscle deformation - contraction or stretching so that it can no longer contract normally. Nutrition of all leg tissues is affected.
symptom
diagnosis
examine
analyze
X-ray
Good to know! For traumatic arthropathy, X-ray examination has great diagnostic value and must be performed.
ultrasound
MRI
treat
- Reduce load as much as possible;
- comply with prescribed modes of transportation;
- Perform therapeutic exercises.

drug
Good to know! Since arthritis can cause severe pain, injections of NSAIDs can work quickly and provide a feeling of relief.
physiotherapy
Laser therapy and physical therapy
Other methods
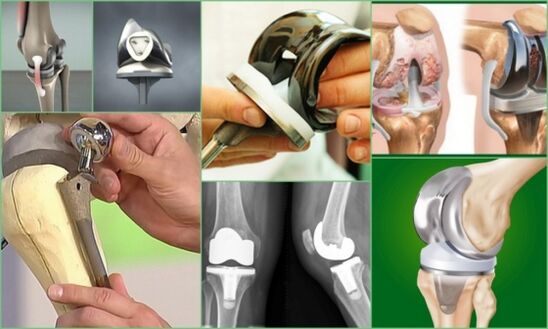
prosthesis
Alternative and traditional medicine
attention! When using unconventional methods, you need to remember that their effectiveness has not been proven.